Austin, TX, USA, Aug. 22, 2025 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) — Custom Market Insights has published a new research report titled “Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Production Market Size, Trends and Insights By Process (Manual iPSC Production, Automated iPSC Production), By Workflow (Cell Culture, Cell Characterization / Analysis), By Product (Consumables & Kits, Automated Platforms), By Application (Drug Development & Discovery, Regenerative Medicine / Tissue Engineering), and By Region – Global Industry Overview, Statistical Data, Competitive Analysis, Share, Outlook, and Forecast 2025 – 2034“ in its research database.
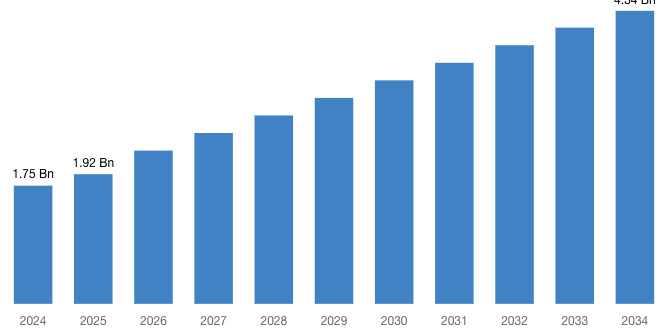
“According to the latest research study, the demand of the global Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Production Market size & share was valued at approximately USD 1.75 Billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 1.92 Billion in 2025 and is expected to reach a value of around USD 4.34 Billion by 2034, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of about 9.5% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034.”
Click Here to Access a Free Sample Report of the Global Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Production Market @ https://www.custommarketinsights.com/request-for-free-sample/?reportid=72414
Overview
According to industry experts at CMI, a major reason for the growth of the Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Production market is the increasing use of these cells in drug discovery, disease modeling, regenerative medicine, and toxicology testing. iPSCs help develop patient-specific cell types that can improve disease representation and predictivity in preclinical research. Continuous advancement in reprogramming technologies and automation, and GMP-compliant manufacturing with respect to scalability, quality, and cost has propelled iPSC-based solutions as a new alternative for clinical translation.
Additionally, government, venture capitalist, and pharmaceutical investments will create accelerated innovation and commercialization. Furthermore, the increasing demand caused by the growing number of chronic and degenerative diseases creates a steady need for new cell-based therapeutic interventions, thus pushing the iPSCs to stand as an essential technology on the way to the development of next-generation, individualized therapeutics.
Key Trends & Drivers
- Potential Therapeutic Applications: Induced pluripotent stem cells can differentiate into virtually any cell type, creating revolutionary opportunities in regenerative medicine. They are increasingly being considered to develop treatments for illnesses such as Parkinson’s, spinal cord injuries, heart failure, and macular degeneration. Developments in cell transplantation, tissue engineering, and organ regeneration are propelling clinical adoption. Clinical trials ongoing into therapies, accompanied by government funding, are helping to fast-track the translation of research into approved therapies. With the rise of chronic and degenerative diseases across the globe, the utmost potential that iPSCs could offer by providing patient-specific, immune-compatible cells to improve treatment outcomes and dictate the sustenance of personalized medicine is worthy of consideration.
- Demand Increasing in Drug Discovery: Increasingly, iPSC-derived cell types find acceptance in the drug discovery and development pipeline in two sectors: pharmaceuticals and biotechnology. Through iPSCs, it becomes possible to develop in vitro physiologically relevant patient-specific systems to test drugs for efficacy, toxicity, and mechanism of action. These systems are more predictive than animal testing, which minimizes late-stage trial failure and spikes in costs of development. iPSCs facilitate research into rare diseases where there is a shortage of patient samples. Although the extent of use, versatility, and scalability of iPSC technology have invited a variety of research and industry alliances, such collaborations could further support high-throughput screening and precision medicine and make iPSCs indispensable in modern drug development strategy.
- Technological Advancement: These advances come in aid of better ways for scaling up iPSC production so that it may further be reproducible and cost-efficient. Some facets of reprogramming technologies have undergone refinements with the goals of achieving high efficiency as well as lowering the risk of genetic instability. Cell culture-based automated and closed-loop bioreactor technologies allow for reproducible large-scale generation of cells intended for research as well as for clinical applications. GMP-grade manufacturing and QC support therapeutic applications in terms of quality and regulatory framework. Having AI and advanced analytics incorporated into bioprocess control will aid yield optimization. All these developments further drive down costs and thereby enable greater adoption of iPSC technologies and hence development in academia, pharmaceutical companies, and clinical research institutions all around the globe.
Request a Customized Copy of the Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Production Market Report @ https://www.custommarketinsights.com/request-for-customization/?reportid=72414
- In an innovation-driven competition: The iPSC market is highly innovation-driven, pushing companies to develop proprietary means of reprogramming, differentiation protocols, and automated manufacturing designs. New media systems, characterization tools, and genetic modification processes continue to shape incumbent positioning. To address high-value therapeutic applications, companies are seeking to create GMP-compliant clinical-grade cell lines. Intellectual property has a crucial role in the dynamics of the market, affecting licensing opportunities and strategic partnerships. Standing out from competitors will rely more and more on the ability to offer high-quality, affordable solutions in large quantities, all while following strict regulations, so that new ideas can lead to both immediate successes and lasting market leadership.
- Strong Collaborative Networks: The collaboration between academia, laboratories, small biotech vendors, and pharmaceutical companies creates opportunities that help the iPSC sector thrive. Academic research brings about new protocols, while industry partners lend their expertise in manufacturing on a large scale, marketing, and regulatory issues. Public-private partnerships and international research consortia exchange knowledge and share resources. They speed up competition between bench innovations and clinical applications, widen global market outreach, and move further toward standardization in production and quality control. By sharing the combined strengths of stakeholders, reducing time-to-market for iPSC-based products, and meeting technical challenges of immense complexity, the stakeholders have enormously improved the commercial and social impact of iPSC technologies the world over.
- Regulatory Influence: Regulatory frameworks play a paramount role in shaping the iPSC production markets. Regulations from various agencies like the FDA, EMA, and PMDA ensure the safety, quality, and traceability of iPSC-derived products, especially if such products are going into the clinics. Compliance with GMP standards is necessary to gain acceptance in the marketplace as well as to win public confidence. But different regulatory requirements across regions become obstacles to global commercialization. Such situations produce delays and add costs to commercialization. Similarly, an encouraging regulatory environment fosters funding of stem cell research by governments, which, in turn, leads to accelerated innovations and quicker uptake of iPSC technologies by the research and therapeutic markets.
Report Scope
| Feature of the Report | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 1.92 Billion |
| Projected Market Size in 2034 | USD 4.34 Billion |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 1.75 Billion |
| CAGR Growth Rate | 9.5% CAGR |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2034 |
| Key Segment | By Process, Workflow, Application and Region |
| Report Coverage | Revenue Estimation and Forecast, Company Profile, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors and Recent Trends |
| Regional Scope | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East & Africa, and South & Central America |